
 |
|
|
Главная --> Промиздат --> Map principle 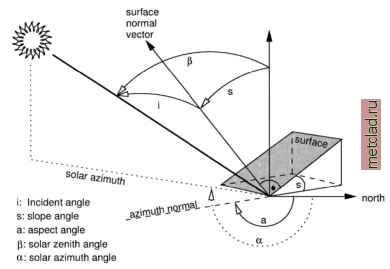 Figure 9.8. Incident angle geometry related to direct solar irradiation onto a tilted surface changes. These changes result from locally changing incident angles between sun radiation and the slope/aspect of the observed object. A generic approach to normalization of the illumination effects is the cosine correction developed by Teillet et al., 1982, and improved, for example, by Sandmeier, 1995. First, the incident angle i is calculated for sloped terrain (tilted surface): cos(/) = cos(P) *cos(.s) -l-sin(P) *sin(.s) *cos(a-a) (9.3) with: i: incident angle between surface normal vector and solar radiation vector [°] P: solar zenith angle from vertical [°] = incident angle for horizontal surface s: surface slope angle to horizontal plane [°] a: solar azimuth angle from north [°] a: aspect angle of surface from north [°] The incident angle geometry is shown in Figure 9.8. The sun position data can be retrieved from the metadata of the data set or calculated for a given date and position with r.sunmask. The normalized direct irradiation Ei. for a Lambertian reflector (which equally reflects in all directions) is calculated as follows: with: El, : normalized direct irradiation [-37-J Xdir observed direct irradiation at ground I Note that this approach may tend to over-correct the brightness levels for steep slopes. It is also based on the assumption that all observed objects behave like Lambertian reflectors. As this is not true for many land use/land cover types, a modified formula, the Minnaert correction model (besides other models) has been developed. It introduces an empirical Minnaert constant based on the image. We do not go into further details here as this approach is described in the remote sensing literature. Formula 9.3 and 9.4 can be implemented in GRASS with r.mapcalc. You need a slope and aspect map for the image area. Remember that aspects are counted counterclockwise from east in r.slope.aspect which requires a reverted orientation and a rotation by 90°. Values for the zenith and azimuth angle of the sun are delivered by r.sunmask. Input map is a radiometrically (gain/bias, eventually atmosphere) corrected channel which will be corrected for the terrain effect. For a simple example, we use the previously geocoded Spearfish SPOT-1 PAN channel (you may also try the SPOT-1 false color composite spot.image, which is delivered in the Spearfish data set). First, we need to calculate the sun position to determine the shadow direction and angle. The image acquisition time was 17:58:50 UTC, date: 5/27/89 (see r.info spot.p). With r.sunmask, we can calculate the sun position. For that, we enter the local time and the time zone: r.sunmask -s y=1989 mon=5 d=27 h=10 min=58 s=50 timez=-7\ elev=elevation.dem out=dummy Using map center coordinates Calculating sun position... (using solpos (V. 11 April 2001) from NREL) 1989.05.27, daynum 147, time: 10:58:50 long: -103.704231, lat: 44.421085, timezone: -7.000000 Solar position: sun azimuth 150.233337, sun angle above horz.(refraction corrected) 64.488976 Sunrise time (without refraction): 04:22 Sunset time (without refraction): 19:22 No map calculation requested. Finished. We now have to re-interpolate the elevation model to 10 m to match the resolution of SPOT-1 PAN image to be terrain effect corrected. Then we calculate the incidence angle map according to Formula 9.3. To speed up the calculations we only work in a subregion: 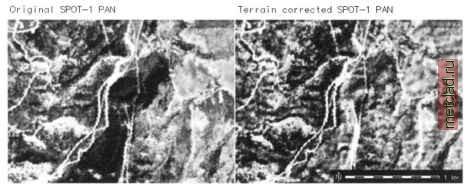 Figure 9.9. Example for cosine correction of terrain effects. Left: uncorrected SPOT-1 PAN image subregion; right: illumination corrected SPOT-1 PAN image subregion (solar azimuth angle: 150°, sun angle above horizon: 64°). Note the area appearing rather dark in the uncorrected image east of the roads. This area is strong inclined with aspect in north-east direction #DEM interpolation to 10m, generate also slope, aspect map: g.region rast=elevation.dem -p n=4924680 s=4922910\ w=590160 e=592590 r.to.sites -a elevation.dem out=elev30 r.info spot.p g.region res=10 -pa s.surf.rst elevSO el=elevl0 as=asl0 sl=sllO ♦generate new aspect map oriented from north, orientation ♦clockwise. We are using an internal variable as: r.mapcalc aslO north=eval(as=360. - aslO + 90.,if(as > 360.,\ as - 360., as)) ♦generate incidence map from sun position: r.mapcalc cos i=cos(90.-64.4)*cos(sllO) + sin(90.-64.4) *\ sin(sllO) * cos (150. - aslO north) r.colors cos i col=grey d. rast cos i d.vect roads col=red ♦generate contour lines from elevlO: r.contour -q elevlO step=20 out=contour10 d.vect contourlO col=green d.vect.labels -m contourlO col=green att=cat We apply this incidence angle map cos i along with the sun angle above the horizon as calculated by r.sunmask to the SPOT-1 PAN image. This minimizes the terrain effects according to Formula 9.4:
|